How Actyx works
Actyx implements local-first cooperation, which in short means that it allows programs on different computers to work together — directly between those computers without the cloud.
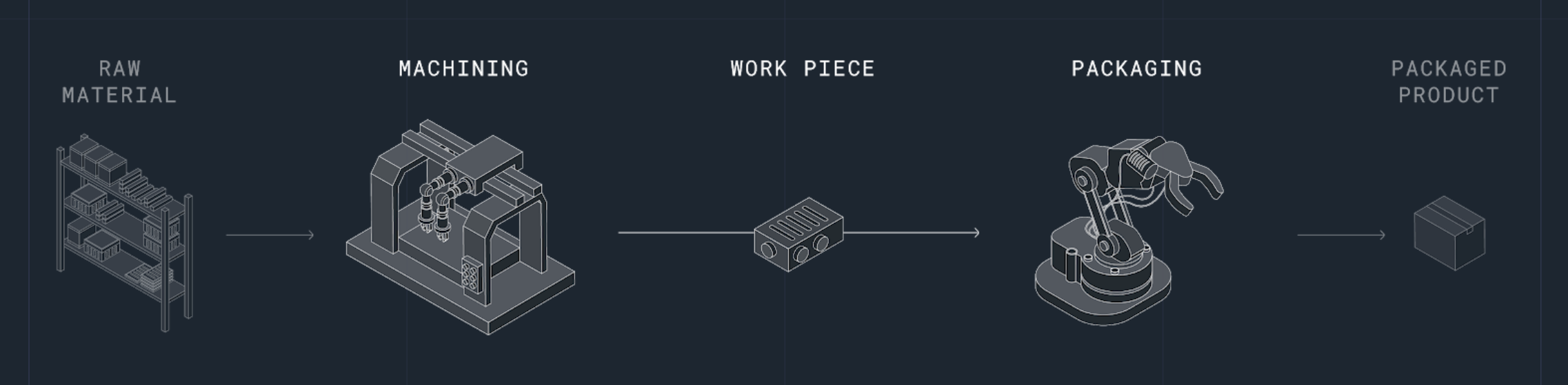
The example process
This conceptual guide explains how Actyx works with a simple example process: A workpiece is processed by a machine, and then packaged by a robot:
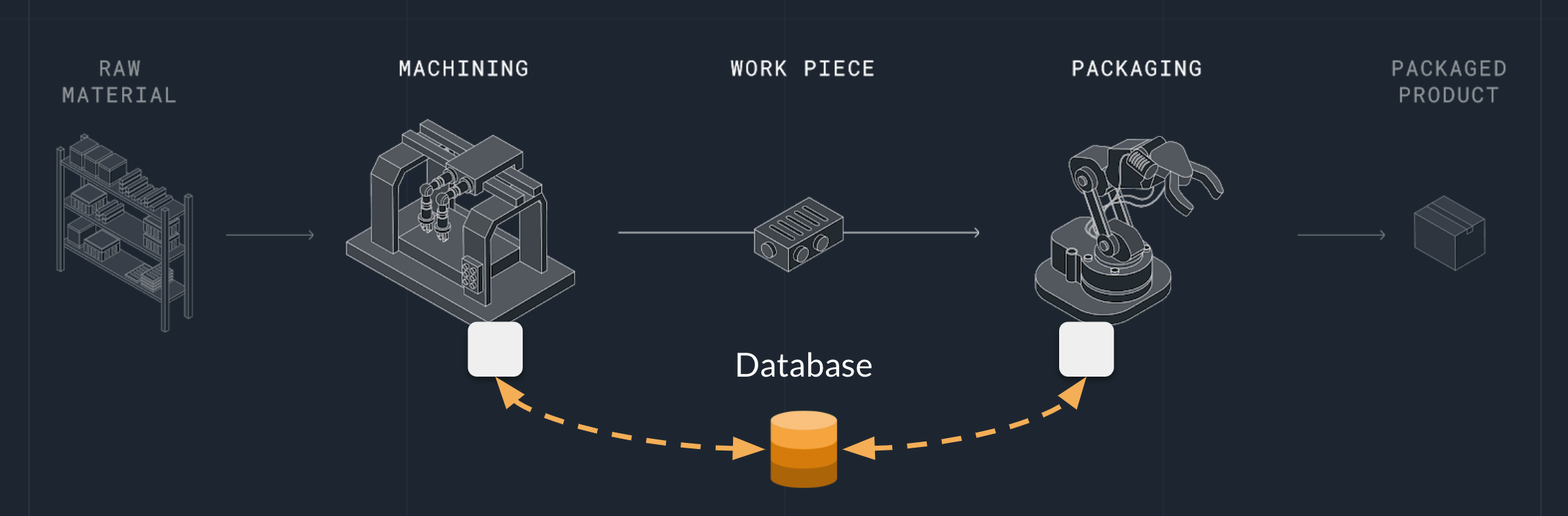
The traditional programming model
Traditionally, you would write two apps, one dealing with each asset. These apps would then be connected to each other with a database or broker:
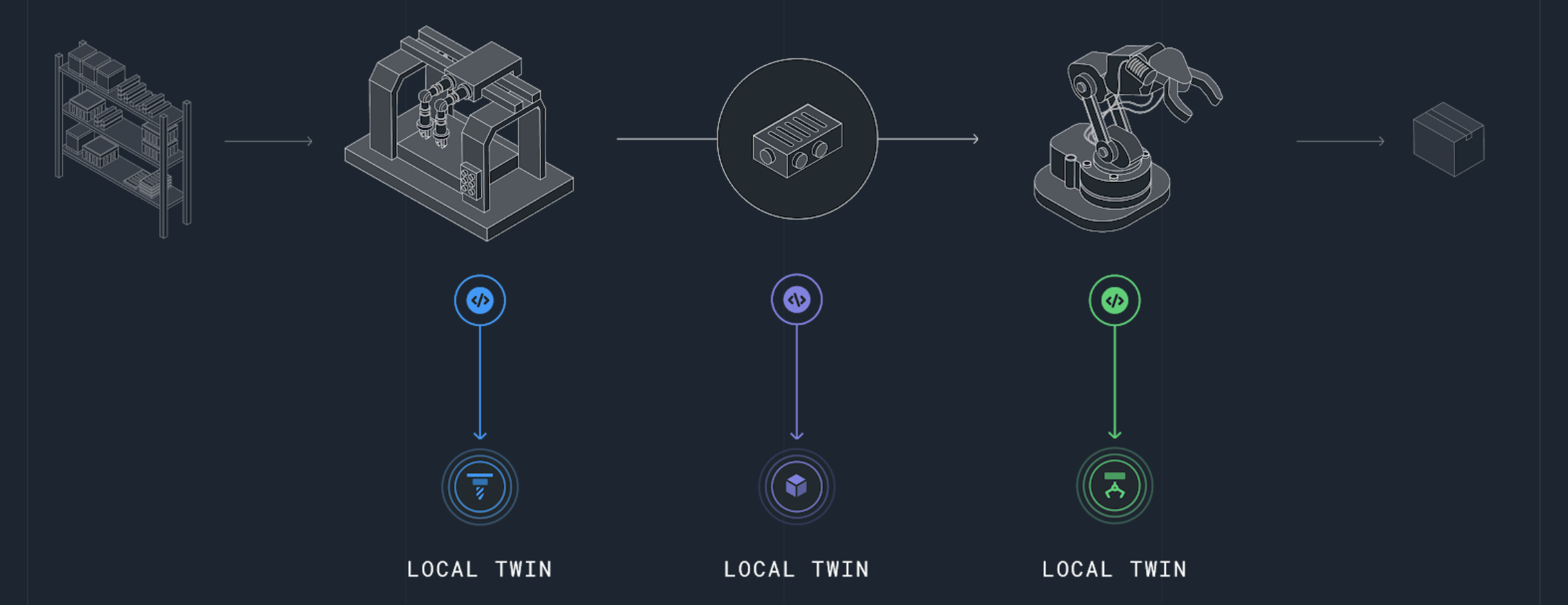
The local-twin programming model
With the Actyx Platform, you program the process as autonomous local twins, that is a digital twin that resides, perceives, and acts locally. These local twins publish and consume events, and develop states based on these events:
There are two different ways in which the business logic can be formulated:
- You can use stateless logic; using the SDK, emit events as they occur in the real world and retrieve information using the Actyx Query Language
- Otherwise, if the local twin models something where your application shall control or coordinate the progression through a sequence of different life cycle states than you can use
machine-runner; please find its docs in the library documentation.
Stateless Local Twins
In the example above, the machine typically manages its own life cycle and the local twin statelessly follows suit:
// first declare tags, optionally with enforced event types
const machine = Tag('machine:4711')
const idle = Tag<{ idle: boolean }>('machineIdle')
const counter = Tag<{ goodPieces: number; scrapPieces: number }>('machineCounter')
machineConnector // assuming this is an EventEmitter
.on('idleStatus', (idle: boolean) => sdk.publish(machine.and(idle).apply({ idle })))
.on('counterUpdate', (goodPieces: number, scrapPieces: number) =>
sdk.publish(machine.and(counter).apply({ goodPieces, scrapPieces })),
)
.on('machined', (workPieceId: string, result: 'good' | 'scrap') =>
sdk.publish(
// WorkPieceTag introduced below
machine.and(WorkPieceTag.withId(workPieceId)).apply({
type: 'machined', machine: '4711', result,
})
)
)
The publish() calls return a Promise that you would typically attach an error handler to.
We leave that out here to focus on the main part.
Obtaining the latest idle state of a machine is then only a matter of running the following AQL query:
const maybeIdle: { idle: boolean } | undefined = (await sdk.queryAql({
query: `
PRAGMA features := aggregate
FROM "machineIdle" & "machine:4711" AGGREGATE LAST(_)
`,
}))
.map(e => e.payload)
.at(0)
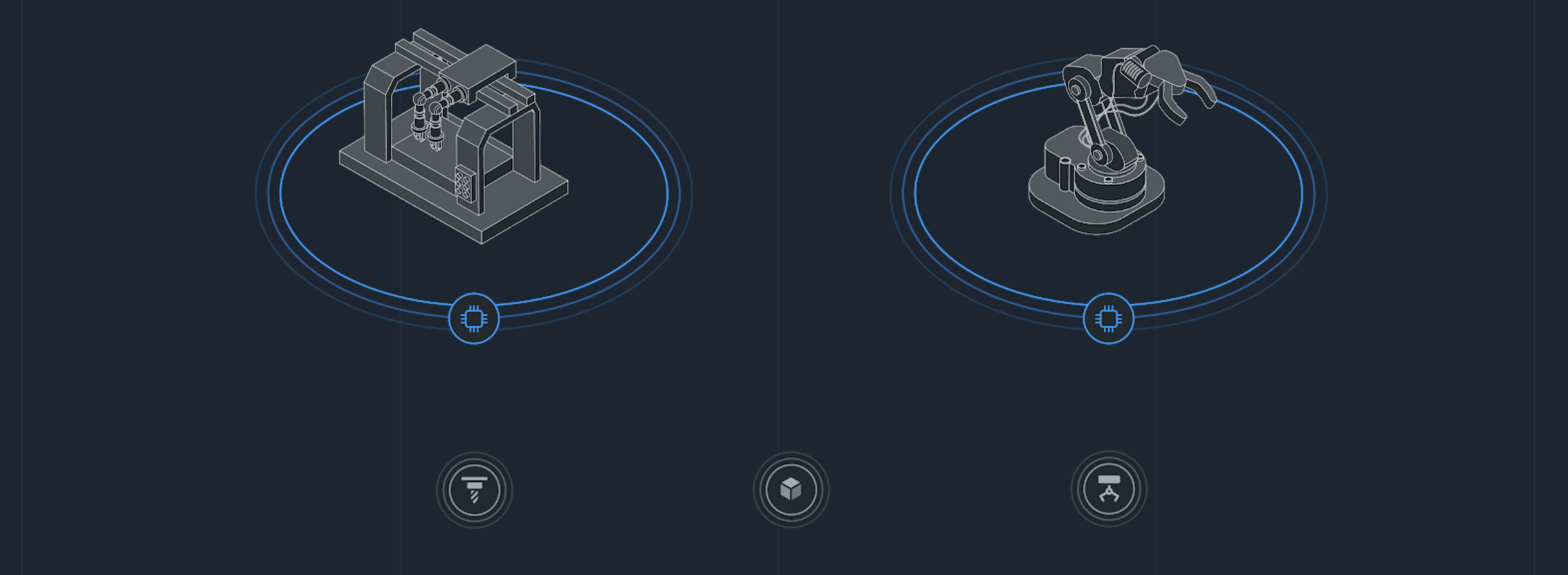
The local computing environment
After you have programmed the local twins, you create local computing environments using edge devices. The local computing environment provides the infrastructure necessary for running local twins. It is a hardware/software combination.
The hardware can be any mobile device, PLC, or PC running Linux, Android, Windows or Docker:
- Tablets: Panasonic, Zebra, Samsung
- PLCs: Phoenix, Beckhoff, Weidmüller
- PCs: any
The software is Actyx. It runs on each device and acts as a decentralized infrastructure which provides data dissemination, data persistence, and runtimes.
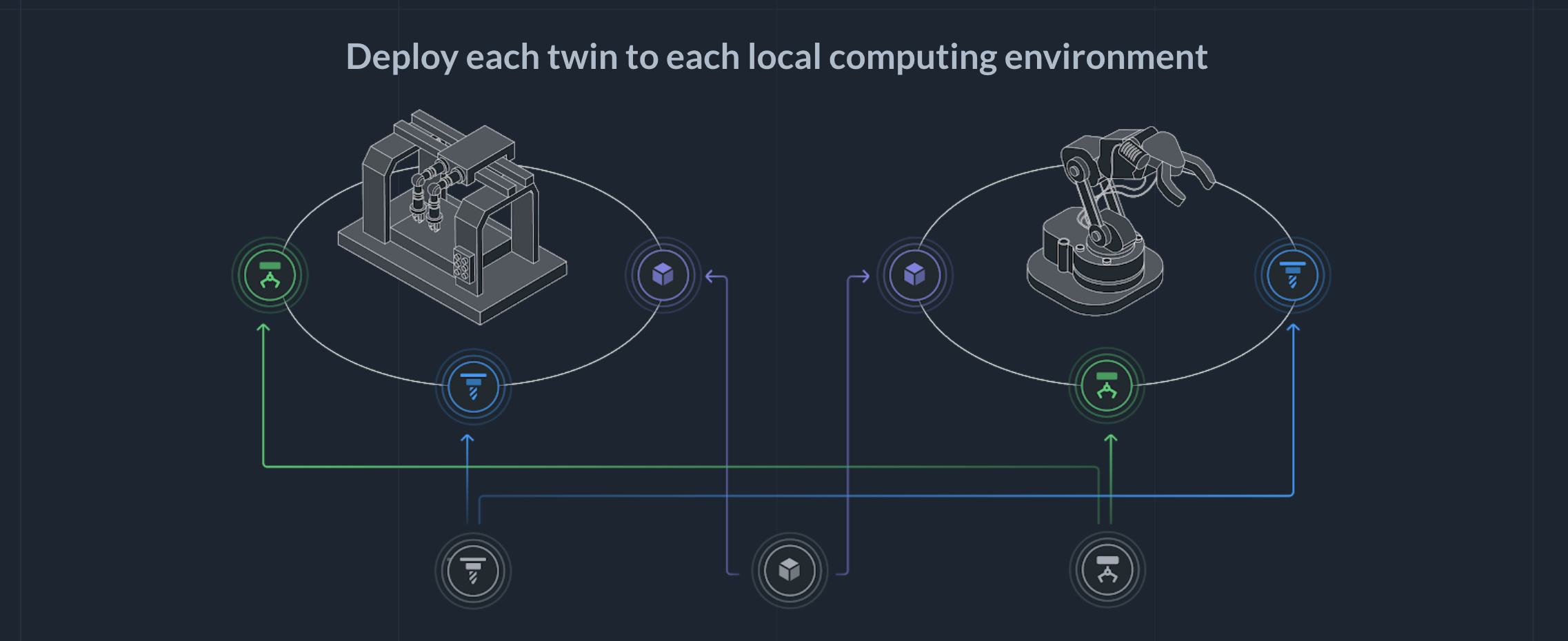
In this example, you could deploy Actyx to a small industrial PC that is connected to the machine (or directly to the machine's PLC) and deploy Actyx to a small industrial PC that you connect to the robot.
Deployment of twins as apps
Twins are packaged into apps that are deployed to the edge devices. Apps are the unit of deployment and contain twins as well as code that interacts with them:
- User interfaces for human interaction
- Machine integrations (e.g. OPC UA, I/Os)
- Software integrations (e.g. ERP, Cloud)
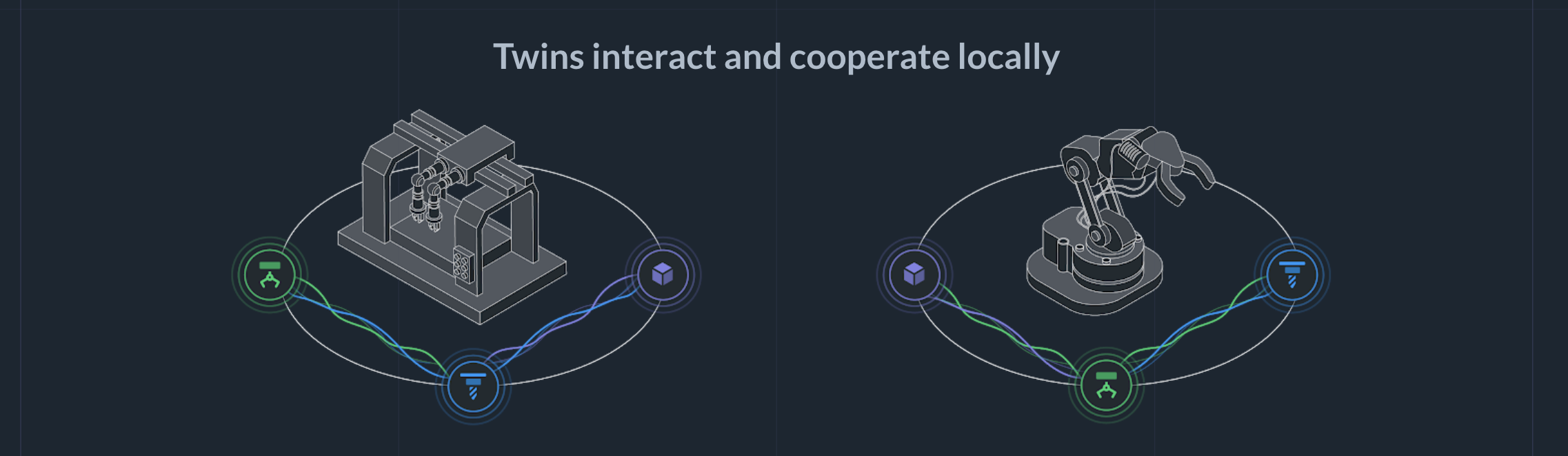
Local interaction
After you have deployed the apps to the edge devices running Actyx, Twins interact and cooperate locally:
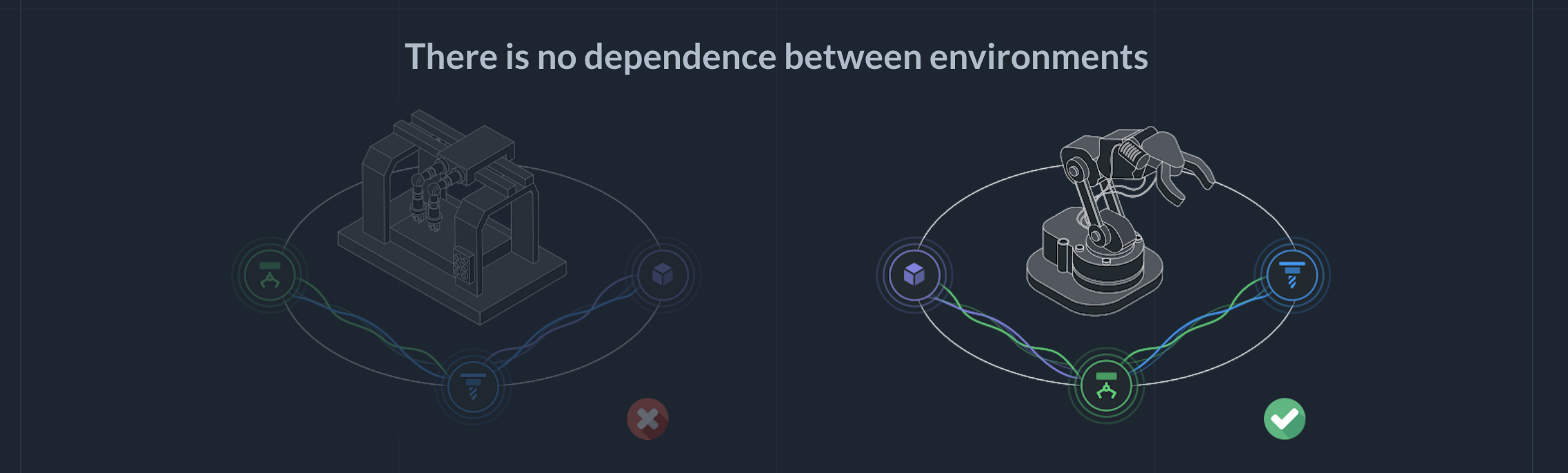
Due to the local interaction of the twins, there is no dependency between environments.
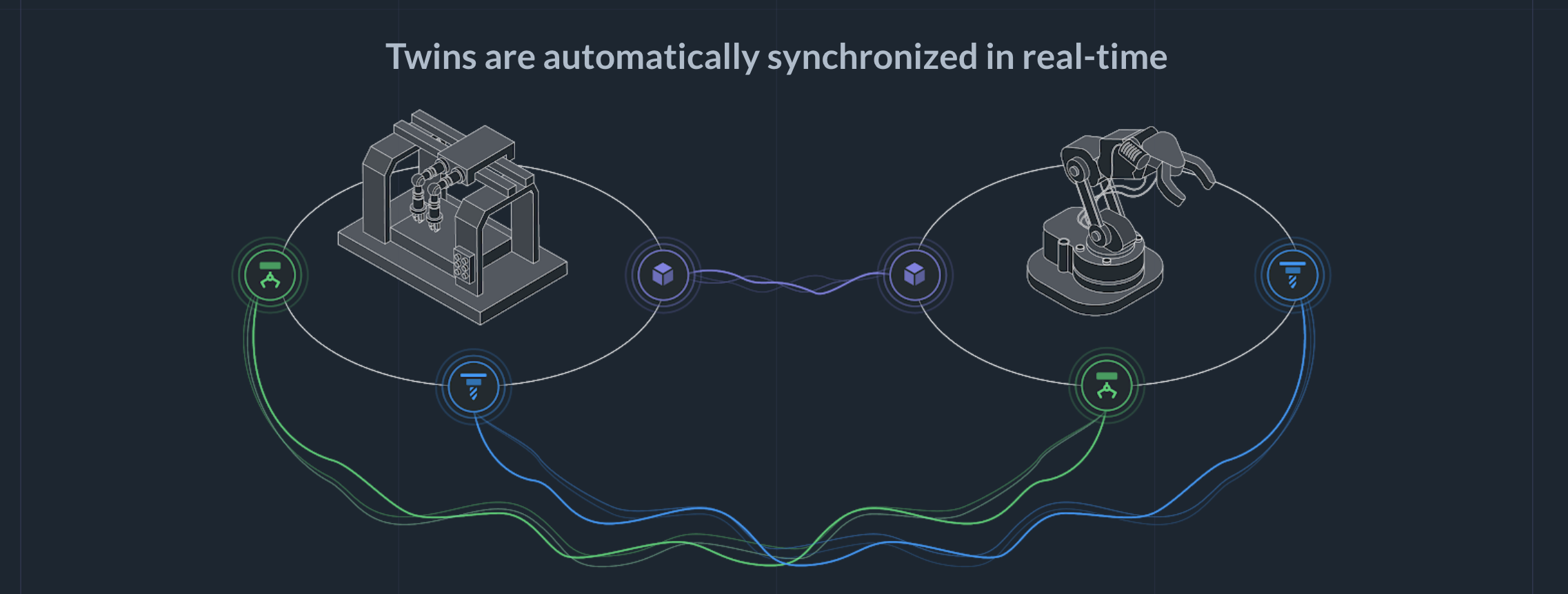
Synchronization of local twins
When edge devices are connected, Actyx automatically synchronizes the twins in real-time:
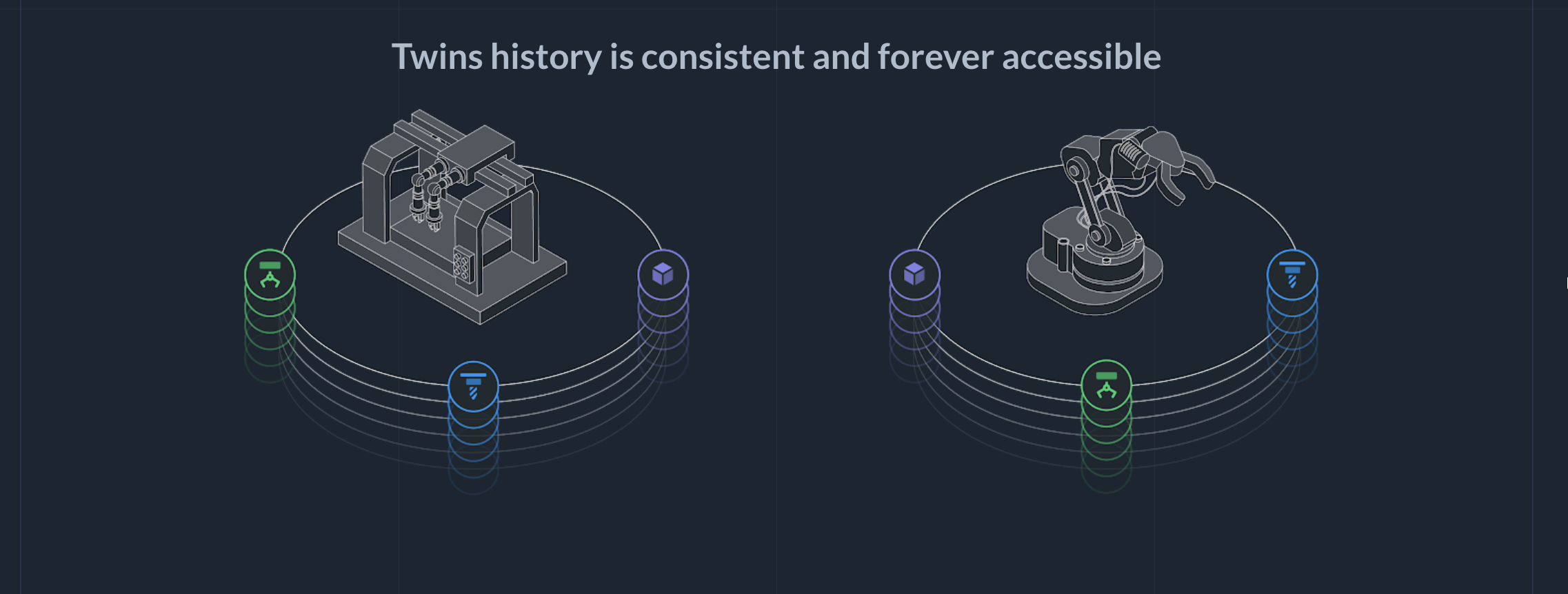
The twins' history is consistent and forever accessible:
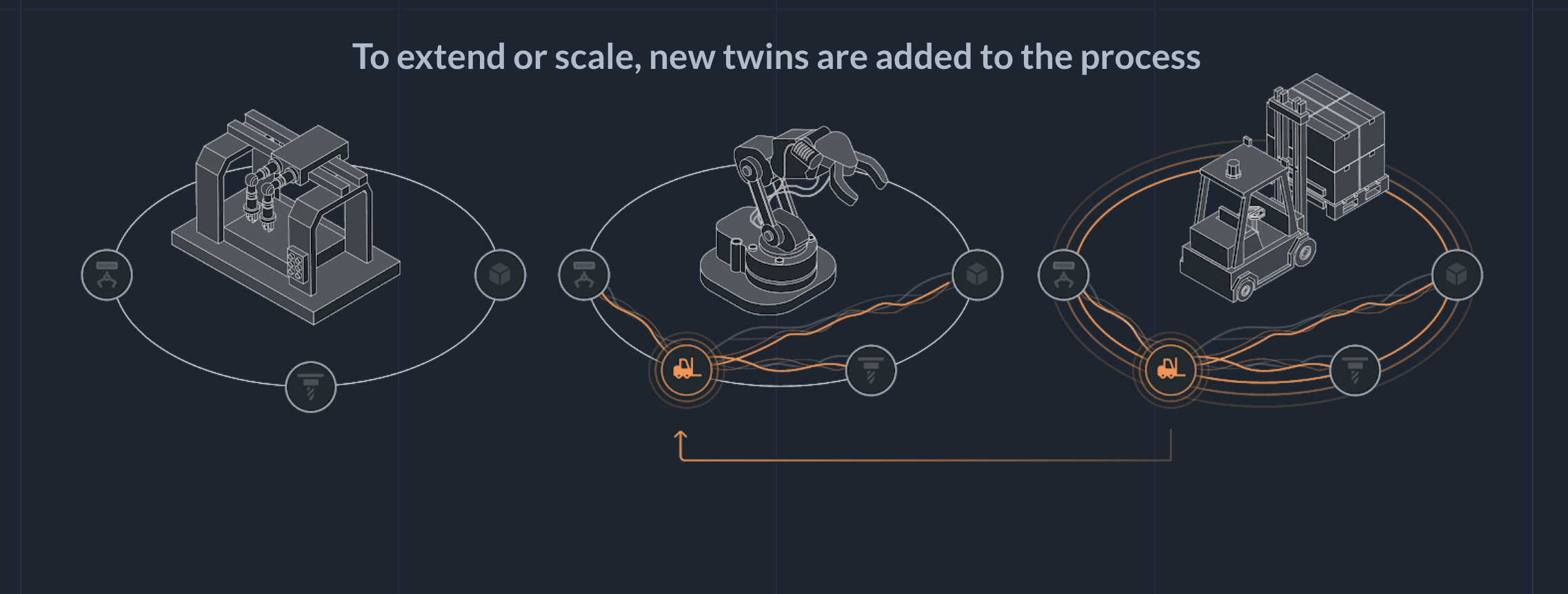
Add new twins to the process
To extend or scale the process, you simply add new local twins: